
 Sickle cell disease is an inherited blood disorder
that is caused by the presence of a mutation in the
gene that
encodes for the
protein, hemoglobin.
Hemoglobin is the protein, which carries oxygen to the tissues.
For patients suffering from sickle cell disease, this genetic
mutation causes the hemoglobin protein to be altered; specifically it
becomes sticky on the surface of the protein.
Different sickle cell hemoglobin molecules stick together and form
long fibers or rods.
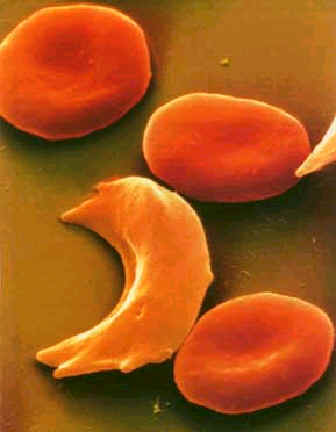
These fibers distort the shape of the red blood cells into sickles
and cause these cells to be less flexible or stiffer in traveling through
the red blood vessels. The
sickled shape impedes the travel of the red blood cells and as a result,
organs and tissues become deprived of oxygen, which can lead to periodic
pain, damage to organs and stroke. (Red
blood cells)
RBC's,
which have undergone the sickling process, are less malleable and rupture
more quickly than regular RBC's leading to anemia.
Sickle cell disease is an inherited blood disorder
that is caused by the presence of a mutation in the
gene that
encodes for the
protein, hemoglobin.
Hemoglobin is the protein, which carries oxygen to the tissues.
For patients suffering from sickle cell disease, this genetic
mutation causes the hemoglobin protein to be altered; specifically it
becomes sticky on the surface of the protein.
Different sickle cell hemoglobin molecules stick together and form
long fibers or rods.
These fibers distort the shape of the red blood cells into sickles
and cause these cells to be less flexible or stiffer in traveling through
the red blood vessels. The
sickled shape impedes the travel of the red blood cells and as a result,
organs and tissues become deprived of oxygen, which can lead to periodic
pain, damage to organs and stroke. (Red
blood cells)
RBC's,
which have undergone the sickling process, are less malleable and rupture
more quickly than regular RBC's leading to anemia.
Main
Page | Next
(Who suffers from it?)